Last Updated on June 13, 2021 by Skillslelo
In 2021, India has 28 States and 8 Union Territories. The capital of India is New Delhi.

Here is the complete list of 28 States and their capitals:
| S.NO | State | Capital |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Amaravati |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| 3 | Assam | Dispur |
| 4 | Bihar | Patna |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Raipur |
| 6 | Goa | Panaji |
| 7 | Gujarat | Gandhinagar |
| 8 | Haryana | Chandigarh |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| 10 | Jharkhand | Ranchi |
| 11 | Karnataka | Bengaluru |
| 12 | Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram |
| 13 | Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal |
| 14 | Maharashtra | Mumbai |
| 15 | Manipur | Imphal |
| 16 | Meghalaya | Shillong |
| 17 | Mizoram | Aizawl |
| 18 | Nagaland | Kohima |
| 19 | Odisha | Bhubaneswar |
| 20 | Punjab | Chandigarh |
| 21 | Rajasthan | Jaipur |
| 22 | Sikkim | Gangtok |
| 23 | Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| 24 | Telangana | Hyderabad |
| 25 | Tripura | Agartala |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | Dehradun |
| 28 | West Bengal | Kolkata |
8 Union Territories and their capitals (if any):
| S.NO | Union Territories | Capital |
| 1 | Andaman and Nicobar Island | Port Blair |
| 2 | Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| 3 | Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | Daman |
| 4 | Delhi | Delhi |
| 5 | Ladakh | NA |
| 6 | Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| 7 | Jammu and Kashmir | NA |
| 8 | Puducherry | Pondicherry |
New States and Union Territories After 1956
The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India’s states and territories, organizing them along linguistic lines.
The additional changes to India’s state boundaries after 1956 are as below:
Maharastra and Gujarat:
In 1960, the bilingual state of Bombay was divided into two separate states – Maharastra for Marathi-speaking speaking people and Gujarat for Gujarati-speaking people.
Dadra and Nagar Haveli:
This territory was converted to a union territory of India by the 10th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1961.
Goa, Daman, and Diu:
India acquired Goa, Daman, and Diu from the Portuguese by means of a police action in 1961. They were constituted as a union territory by the 12th Constitutional Amendment Act 1962.
In 1987, Goa has conferred a statehood.
Consequently, Daman and Diu were made a separate union territory.
Puducherry:
In 1954, the French handed over Puducherry to India. Till 1962, it was administered as an ‘acquired territory’.
Puducherry was made a union territory by the 14th Constitutional Amendment Act.
Nagaland:
In 1963, the State of Nagaland was formed by taking the Naga Hills and Tuensang area out of the state of Assam.
Haryana, Chandigarh, and Himachal Pradesh
In 1966, the state of Punjab was bifurcated to create Haryana, the 17th state of Indian Union and the union territory of Chandigarh.
In 1971, the union territory of Himachal Pradesh was elevated to the status of a state. (18th state of Indian Union)
Manipur, Tripura and Meghalaya:
In 1972, the political map of Northeast India underwent a major change. The two Union Territories of Manipur and Tripura and the sub-state of Meghalaya got statehood.
Sikkim:
Sikkim was made a full-fledged state of the Indian Union by the 36th Constitutional Amendment Act 1975.
Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh and Goa:
In 1987, three new states of Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, and Goa came into being as the 23rd, 24rth, and 25th states of Indian Union respectively.
Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, and Jharkhand:
In 2000, three more new states of Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, and Jharkhand were created out of the territories of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar respectively.
Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh:
In August 2019, the Parliament of India passed the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, which contains provisions to reorganize the state of Jammu and Kashmir into two union territories; Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, effective from 31 October 2019.
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu:
Later that year in November, the Government of India introduced legislation to merge the union territories of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli into a single union territory to be known as Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, effective from 26 January 2020.
Change In the Name of States and UT:
The United Province was the first state to have a new name. It was renamed Uttar Pradesh in 1950.
In 1969, Madras was renamed Tamil Nadu.
In 1973, Mysore was renamed Karnataka. In the same year, Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands were renamed Lakshadweep.
In 2006, Uttaranchal was renamed Uttarakhand. In the same year, Pondicherry was renamed Puducherry.
Old and New Names of States & UTs
| Old | New | Year of Change |
| United Province | Uttar Pradesh | 1950 |
| Madras | Tamil Nadu | 1969 |
| Mysore | Karnataka | 1973 |
| Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands | Lakshadweep | 1973 |
| Uttaranchal | Uttarakhand | 2006 |
| Pondicherry | Puducherry | 2006 |
States and Union Territories:
The states are the members of the federal system in India and share the distribution of power with Centre.
On the other hand, the union territories are those areas which are under the direct control and administration of the Central government.
At present, there are 28 states and 8 union territores.
The union territories have been created for a variety of reasons. See below;
1 . Political and administrative considtration: Delhi and Chandigarh
2. Cultural distinctiveness- Puducherry, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
3. Strategic importance- Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep
Comparing States and Union Territories
| States | Union Territories |
| The relationship with Centre is federal. | The relationship with Centre is unitary. |
| They share a distribution of power with the Centre. | They are under the direct control and administration of the Centre. |
| They have autonomy. | They do not have any autonomy. |
| There is uniformity in their administrative set-up. | There is no uniformity in their administrative set-up. |
| The Executive head is knowns as the governor. | The executive head is known by various names- Administrator, lieutenant governor or chief commissioner. |
| A governor is a constitutional head of the state. | An administrator is an agent of the president. |
India Political Map
The India Political map shows all the states and union territories of India along with their capital cities.
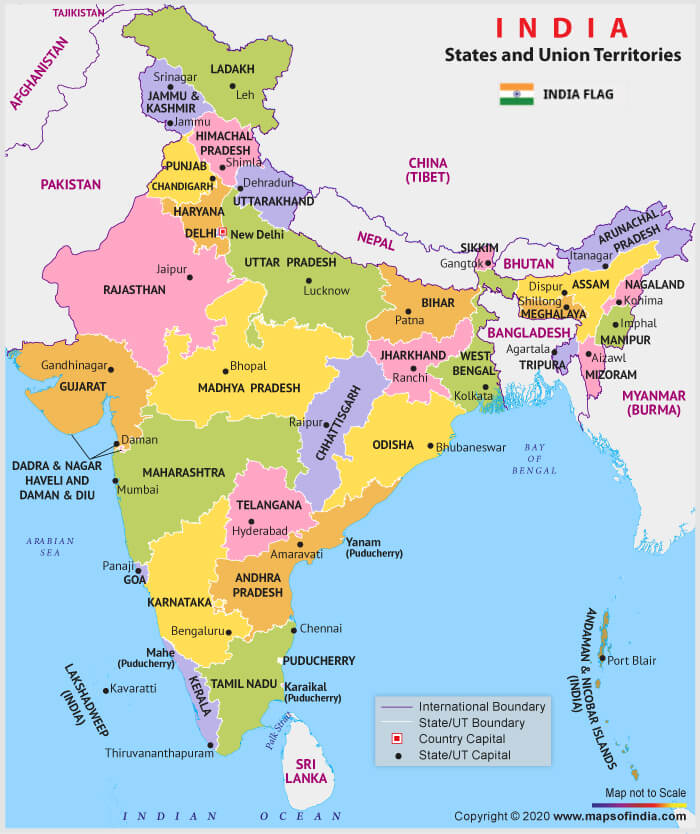
Image Source: https://www.mapsofindia.com